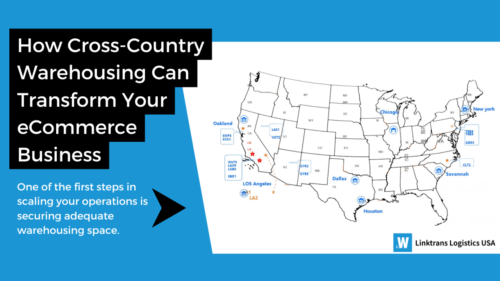
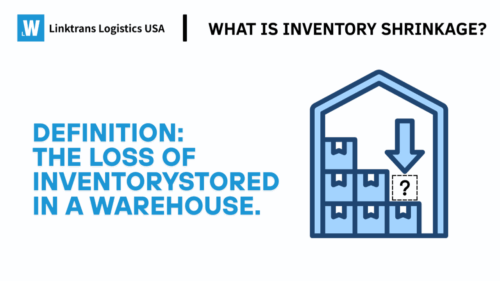
-
English
-
Japanese
-
Korean

General Freight Terms
3PL (Third-Party Logistics): A company that provides outsourced logistics services, including warehousing, transportation, and fulfillment.
Bill of Lading (BOL): A legal document issued by a carrier to a shipper detailing the type, quantity, and destination of goods being transported. It serves as a shipment receipt and a contract of carriage.
Carrier: The company or individual responsible for transporting goods (e.g., trucking companies, shipping lines, airlines).
Consignee: The individual or business receiving the shipment.
Shipper: The individual or business sending the shipment.
Freight Forwarder: A company that organizes shipments for individuals or businesses, often acting as an intermediary between the shipper and carrier.
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms): Standardized terms defining the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international trade, such as who pays for shipping, insurance, and customs.
Freight Costs and Charges
FOB (Free on Board): Indicates whether the seller or buyer is responsible for goods during transit. For example, "FOB Origin" means the buyer assumes responsibility once the goods leave the seller's location.
Freight Collect: The consignee is responsible for paying the freight charges.
Freight Prepaid: The shipper pays the freight charges before the shipment is delivered.
Accessorial Charges: Additional fees for extra services, such as inside delivery, liftgate service, or residential delivery.
Dimensional Weight (DIM Weight): A pricing method based on the shipment's volume rather than its actual weight, often used for lightweight but bulky shipments.
Shipping Methods and Modes
LTL (Less Than Truckload): A shipping method for smaller freight that doesn’t require a full truckload. Multiple shipments from different shippers are combined in one truck.
FTL (Full Truckload): A shipping method where a single shipment occupies the entire truck, typically used for large or high-volume shipments.
Intermodal Shipping: The use of multiple modes of transportation (e.g., truck, rail, ship) to move goods.
Drayage: The transportation of goods over short distances, often between ports, rail terminals, and warehouses.
Air Freight: Shipping goods via air transport, typically used for high-value or time-sensitive shipments.
Ocean Freight: Shipping goods via sea transport, often used for international trade.
Freight Documentation
Packing List: A document detailing the contents of a shipment, including item descriptions, quantities, and weights.
Commercial Invoice: A document used in international shipping that includes details about the goods, their value, and the terms of sale.
Certificate of Origin (COO): A document certifying the country in which the goods were manufactured, often required for customs clearance.
Manifest: A detailed summary of the shipment, including contents, weight, and destination, used by the carrier.
Freight Units and Measurements
Pallet: A flat platform used to stack goods for easy handling and transport.
TEU (Twenty-Foot Equivalent Unit): A standard measure for containerized cargo, based on a 20-foot-long container.
CBM (Cubic Meter): A measurement of volume used in freight to calculate space occupied by goods.
Gross Weight: The total weight of the shipment, including packaging and pallets.
Net Weight: The weight of the goods themselves, excluding packaging.
Customs and International Shipping
Customs Clearance: The process of submitting documentation and paying duties or taxes to allow goods to enter or leave a country.
Harmonized System (HS) Code: A standardized code used to classify goods for customs purposes.
Duty: A tax imposed on goods imported into a country.
Bonded Warehouse: A storage facility where imported goods can be stored without paying customs duties until they are sold or moved.
Freight Handling and Delivery
Liftgate Service: A service where a hydraulic lift is used to load or unload heavy goods from a truck.
Last Mile Delivery: The final step of the shipping process, where goods are delivered directly to the customer’s location.
Cross-Docking: A practice where goods are unloaded from one truck and immediately loaded onto another for delivery, minimizing storage time.
White Glove Service: A premium delivery service that includes unpacking, assembly, and placement of goods at the final destination.
Freight Risk and Insurance
Freight Insurance: Coverage that protects against loss or damage to goods during transit.
Freight Claim: A formal request for compensation filed by a shipper or consignee when goods are lost or damaged in transit.
Force Majeure: A clause in contracts that absolves parties from liability for unforeseen events like natural disasters or strikes that prevent fulfillment of obligations.